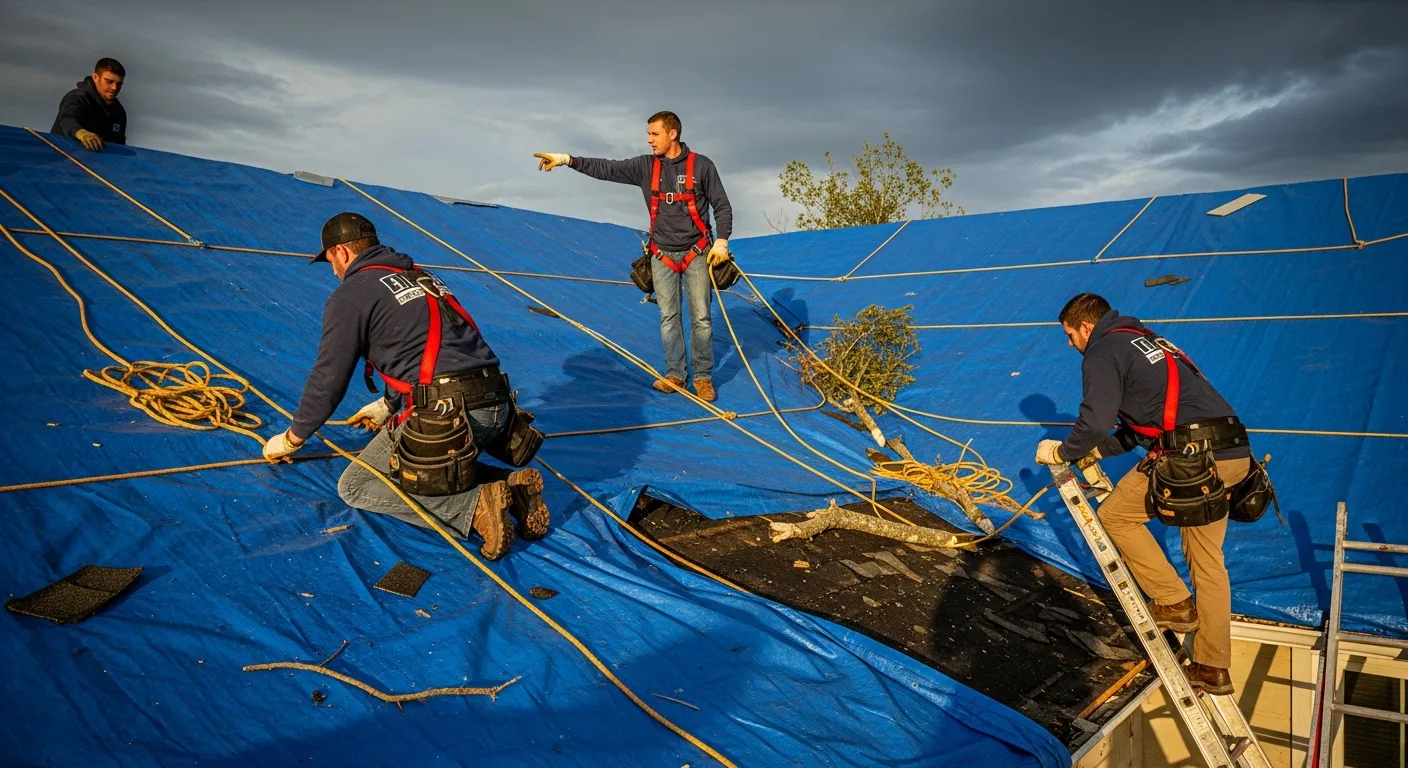
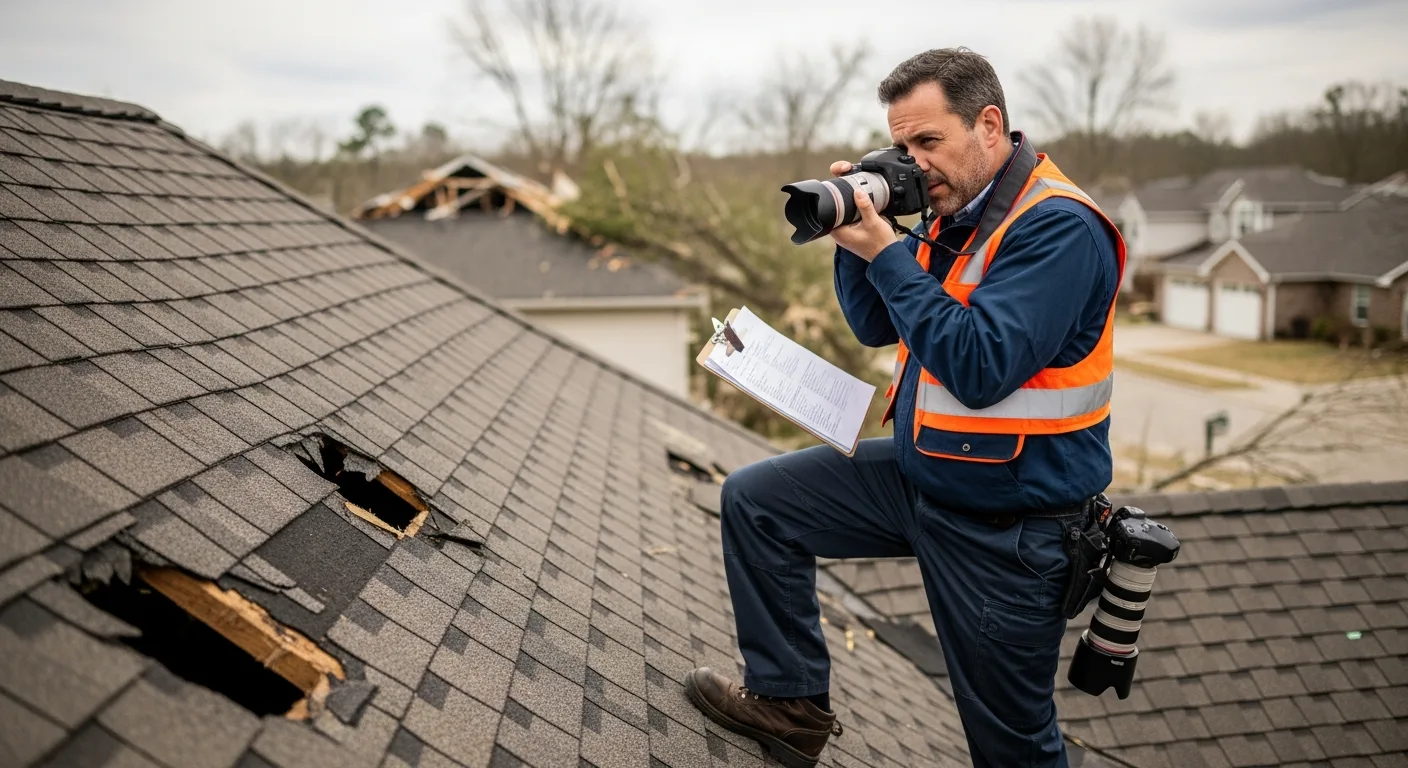
Hailstorms are among the most destructive weather events that can impact roofing systems, but the way hail damages commercial and residential roofs varies significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for property owners in Amarillo, Texas, where severe weather is a common occurrence. While both roof types can suffer substantial damage from hail, the distinct characteristics of commercial and residential roofing materials, installation methods, and structural designs create unique vulnerabilities and damage patterns.
Understanding Hail Impact Mechanics
When hailstones strike a roof, the damage occurs through a combination of impact force, temperature differential, and material compression. The size, density, and velocity of hailstones determine the severity of impact, while the roofing material's composition and installation method influence how that impact translates into actual damage. According to the National Roofing Contractors Association, hail damage can range from minor granule loss to complete membrane penetration, depending on these variables.
The angle of impact also plays a crucial role in damage patterns. Wind-driven hail creates different damage signatures compared to vertically falling hail, and this factor affects commercial and residential roofs differently due to their varying heights, slopes, and surrounding structures. The Federal Emergency Management Agency emphasizes that understanding these impact mechanics is essential for proper damage assessment and repair planning.
Commercial Roofing System Vulnerabilities
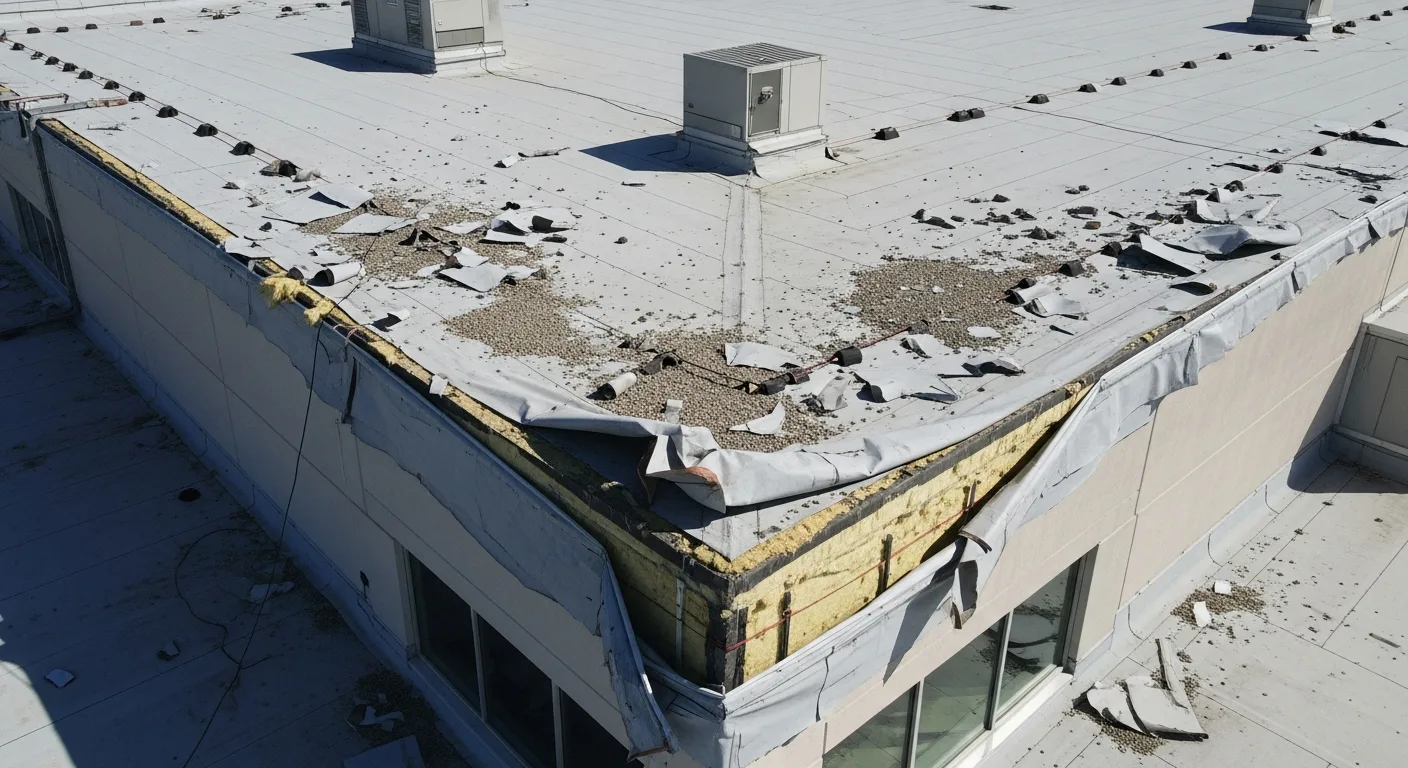
Commercial roofs typically feature low-slope or flat designs with membrane-based systems such as EPDM, TPO, modified bitumen, or built-up roofing. These systems present unique vulnerabilities to hail damage that differ significantly from residential applications. The large, uninterrupted surface areas common in commercial roofing provide extensive exposure to hailstorms without the protective elements found on residential structures.
Membrane System Damage Patterns
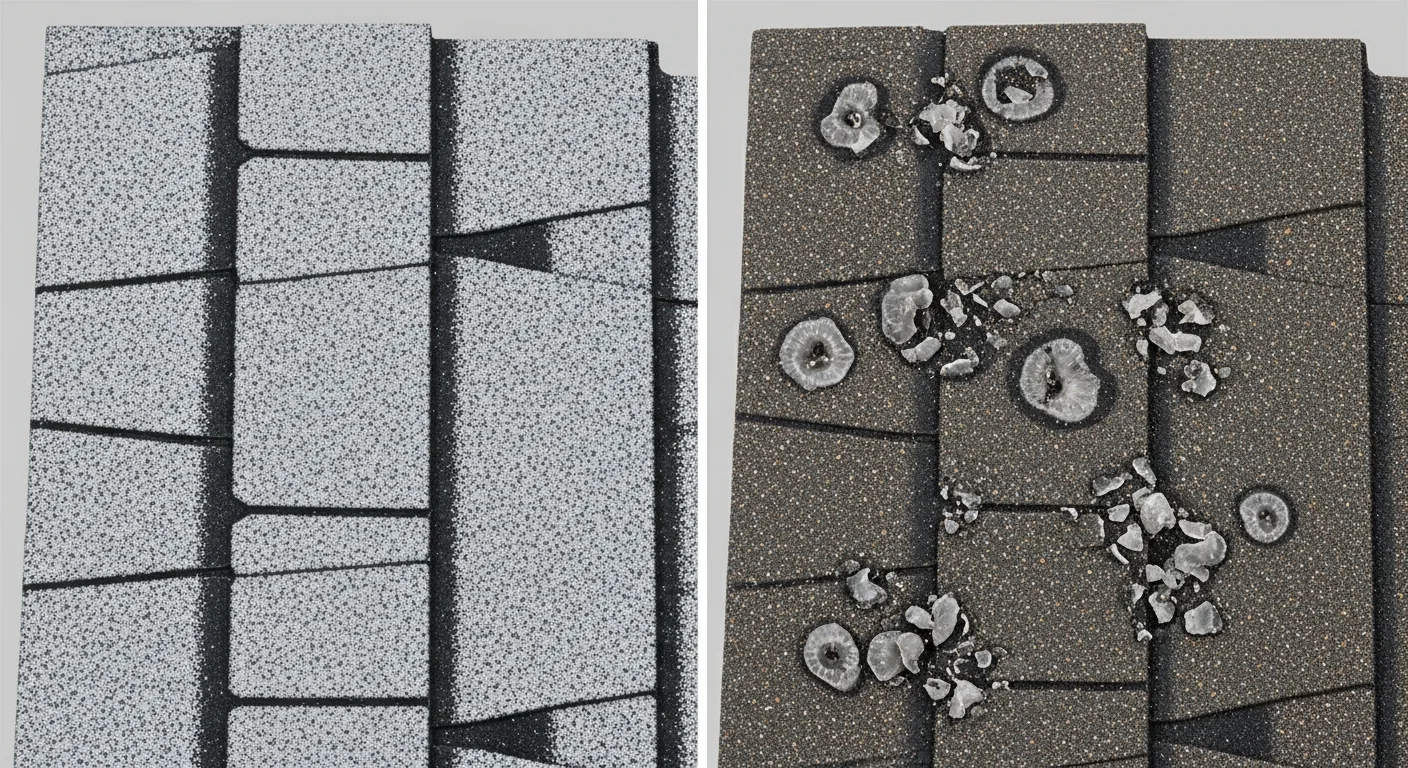
Single-ply membrane systems like TPO and EPDM are particularly susceptible to punctures and tears from larger hailstones. The relatively thin profile of these materials, typically ranging from 45 to 80 mils in thickness, offers limited protection against high-impact hail. When hailstones strike these membranes, they can create immediate punctures or cause microscopic tears that develop into leaks over time.
Modified bitumen systems, while offering multiple layers of protection, can experience different damage patterns. The granulated surface may suffer extensive granule loss, exposing the underlying asphalt layers to UV radiation and accelerating deterioration. The GAF Commercial Roofing division notes that this type of damage often requires comprehensive membrane replacement rather than spot repairs.
Drainage and Equipment Considerations
Commercial roofs contain numerous penetrations for HVAC equipment, drainage systems, and utility connections. These areas create additional vulnerability points where hail damage can compromise sealing systems and flashings. Large HVAC units and equipment screens can also be damaged by hail, creating secondary issues that affect overall roof performance.
The low-slope design of most commercial roofs means that proper drainage is critical for preventing water accumulation. Hail damage to drainage systems, including gutters, downspouts, and roof drains, can create ponding issues that exacerbate initial damage and lead to more extensive problems.
Residential Roofing System Impact
Residential roofs predominantly use steep-slope designs with asphalt shingles, though tile, slate, and metal roofing systems are also common. The steeper pitch and smaller surface areas of residential roof systems create different hail damage patterns and vulnerabilities compared to commercial applications.
Asphalt Shingle Damage Characteristics
Asphalt shingles, the most common residential roofing material, exhibit specific damage patterns when struck by hail. Initial impact typically causes granule loss, which exposes the underlying asphalt mat to UV radiation and weather elements. This granule displacement is often the first visible sign of hail damage and can significantly reduce the shingle's protective capabilities.
More severe hail impacts can cause mat fractures, where the fiberglass or organic mat within the shingle cracks or breaks. These fractures may not be immediately visible but can lead to premature shingle failure and water infiltration. Owens Corning's hail damage research demonstrates that impact severity correlates directly with hailstone size and the age of the shingles.
Structural Component Considerations
Residential roofs include various components that can suffer hail damage beyond the primary roofing material. Gutters, downspouts, vent covers, and skylights are particularly vulnerable to denting and cracking. These components often require replacement even when the primary roofing material sustains only minor damage.
The steep slope of residential roofs provides some protection by allowing hailstones to glance off rather than delivering direct impact. However, this same slope can create areas of concentrated impact where architectural features or equipment create flat surfaces perpendicular to hailstone trajectory.
Comparative Damage Assessment Challenges
Assessing hail damage on commercial versus residential roofs requires different approaches and expertise. Commercial roof inspections often require specialized equipment to safely access large, flat surfaces and may involve core sampling to determine membrane integrity. The Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety has conducted extensive research on hail damage assessment techniques for both roof types.
Documentation and Insurance Considerations
Commercial roof damage assessment typically involves more comprehensive documentation due to the higher replacement costs and complex insurance policies involved. Thermal imaging, moisture detection, and detailed photographic documentation are standard practices for commercial hail damage claims.
Residential assessments, while less complex, still require thorough documentation to support insurance claims. The distributed nature of residential hail damage often means that multiple shingles and components require evaluation, making the assessment process time-intensive despite the smaller overall roof area.
Repair and Replacement Strategies
The approach to hail damage repair differs significantly between commercial and residential applications due to material properties, installation methods, and performance requirements. Commercial repairs often involve large-scale membrane replacement or overlay systems, while residential repairs may focus on individual shingle replacement or partial roof sections.
Commercial Repair Complexities
Commercial hail damage repairs frequently require coordination with building operations to minimize business disruption. The interconnected nature of commercial roofing systems means that localized damage often necessitates broader repairs to maintain system integrity. Firestone Building Products emphasizes the importance of comprehensive system evaluation following hail events.
Residential Repair Efficiency
Residential hail repairs benefit from the modular nature of shingle systems, allowing for targeted replacement of damaged components. However, matching existing materials and maintaining aesthetic consistency can present challenges, particularly with discontinued product lines or weathered materials.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
While hail damage cannot be completely prevented, understanding the different vulnerabilities of commercial and residential roofing systems allows for targeted mitigation strategies. The Department of Energy's cool roof initiatives include hail-resistant technologies that benefit both commercial and residential applications.
Commercial building owners can invest in impact-resistant membrane systems and protective screens for equipment, while residential property owners can choose Class 4 impact-resistant shingles and maintain proper attic ventilation to reduce thermal stress that makes materials more susceptible to hail damage.
Regular maintenance and prompt repair of minor damage help both roof types maintain their integrity and resist future hail events. Professional inspection following severe weather events ensures that hidden damage is identified before it leads to more extensive problems, regardless of whether the roof is commercial or residential in nature.
In the Texas Panhandle, where National Severe Storms Laboratory research indicates hailstorms can produce stones exceeding 2 inches in diameter with velocities over 100 mph, commercial flat roofs face unique challenges compared to residential pitched systems. The membrane systems commonly used in commercial applications, including TPO, EPDM, and PVC, respond differently to hail impact than traditional asphalt shingles. While residential shingles may show visible granule loss or cracking, commercial membranes often sustain punctures or tears that can lead to immediate water infiltration.
Commercial roofing systems typically feature larger uninterrupted surfaces that create greater exposure to hail damage. Carlisle SynTec systems and other single-ply membranes rely on heat-welded seams that can become vulnerable points during severe hail events. The lack of slope on most commercial roofs means hailstones don't deflect as readily as they do on steeper residential roofs, resulting in more direct impact energy transfer. Additionally, the thermal expansion and contraction cycles common in Amarillo's climate—with summer temperatures exceeding 100°F and winter lows below freezing—can pre-stress membrane materials, making them more susceptible to hail damage.
Residential roofing systems benefit from steeper slopes that help deflect hail impact, but material composition creates different vulnerability patterns. Traditional asphalt shingles may lose protective granules upon impact, while TAMKO's impact-resistant shingles incorporate polymer-modified asphalt designed to withstand UL 2218 Class 4 impact testing. The overlapping installation pattern of residential shingles provides multiple layers of protection, whereas commercial membranes typically offer a single barrier layer.
According to Insurance Institute for Business & Home Safety testing protocols, hail damage assessment requires different evaluation criteria for commercial versus residential systems. Commercial roof inspections focus on membrane integrity, seam condition, and fastener security, while residential assessments examine granule loss patterns, exposed mat, and shingle tab integrity. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate damage evaluation and proper repair specifications in the Texas Panhandle's challenging weather environment.